Connectors are a common component in electronic devices used to join circuits together so that current can be smoothly transmitted to ensure proper operation of the device. They are used in a wide variety of applications and feature reliability, high-speed transmission, high-density connections, and durability to support device performance and functionality.
When it comes to electrical connections in automotive and industrial environments, it is important to understand the differences between sealed and unsealed connectors. This article focuses on the subtle differences between these two types of connectors.
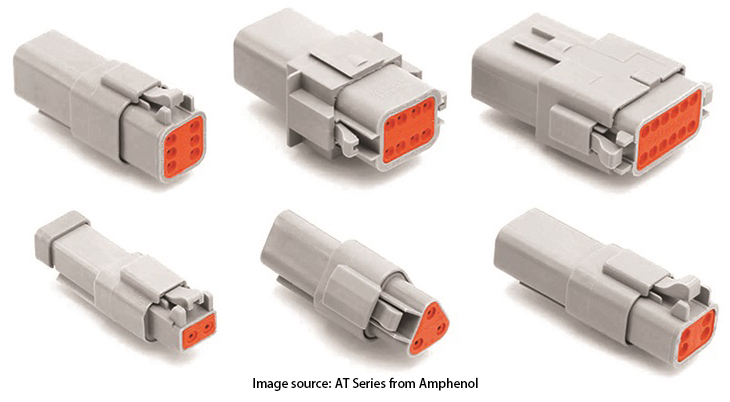
Amphenol AT Series connectors provide high performance for use in a variety of interconnect applications,
suitable for heavy equipment, agricultural, automotive, military, alternative energy and other demanding interconnect architectures,
and feature IP68/69K ratings to protect against water and Dust entry is suitable for both exterior and cabin applications and enables higher sealing specifications upon request.
1. Definition and Application Scenarios
Sealed connectors are designed for electrical and signal transmission and are sealed against water, dust, and corrosion. They provide reliable connections in harsh environments and protect internal circuits from the external environment. Sealed connectors are widely used in automotive, aerospace, marine, military, industrial equipment outdoor electronics, etc. These applications require high sealing and reliability of connectors.
Non-sealed connectors, on the other hand, do not have a sealed design, and the connectors are not specially treated to prevent the ingress of liquids or dust. Non-sealed connectors are usually used in household appliances, IT equipment internal slot connections automotive internal unimportant wiring connections, etc. These applications do not require a high level of protection, and the working environment is less demanding.
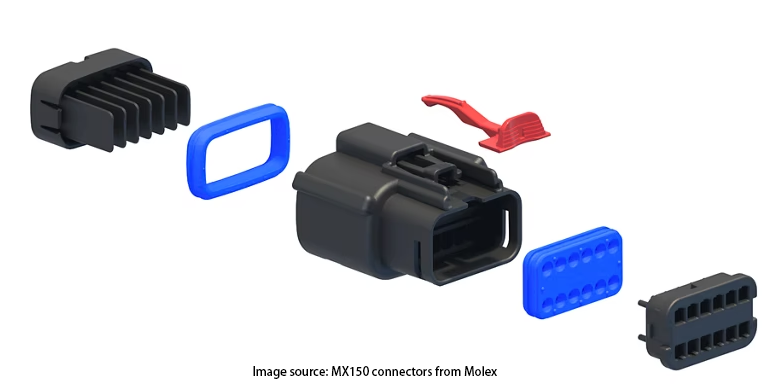
Molex’s MX150 connector saves space by eliminating the need for a separate cable seal and protects,
securely holds, and provides strain relief for wire seal interfaces in automotive, commercial vehicle, industrial, vehicle, and equipment applications.
2. Functional characteristics
Sealing performance: Sealed connectors use special sealing materials, sealing rings, or structures to prevent external substances such as water, dust, and chemicals from entering the interior. This ensures reliable protection against corrosion and short circuits. Non-sealed connectors have a simpler structure and do not use seals or other sealing devices, so the protection is lower.
Protection level: Sealed connectors are waterproof, can work underwater or in wet environments, and comply with specific waterproof standards, such as IP67 or IP68. non-sealed connectors have a lower level of protection and are not suitable for harsh environments, such as outdoor, wet, or corrosive environments.
Special designs: Sealed connectors usually have special mating and locking mechanisms to ensure a strong and reliable connection and are therefore more costly. They may contain additional sealing components such as O-rings or sealing threads. Non-sealed connectors do not require these additional components and are relatively inexpensive to manufacture.
Dust resistance: Sealed connectors effectively prevent the ingress of fine particles, dust, and other contaminants, preventing contamination and electrical problems at the point of contact. Non-sealed connectors have open connectors that help ventilate heat and reduce efficiency problems caused by elevated temperatures and are therefore less dust resistant.
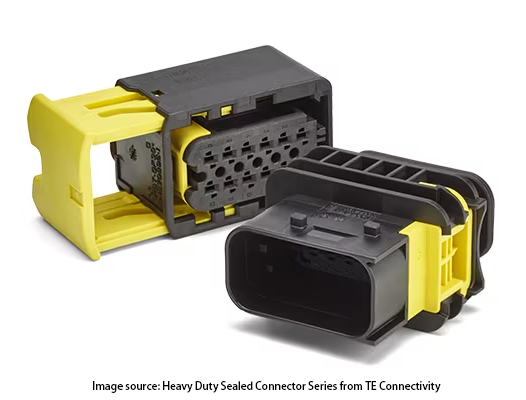
TE Connectivity’s heavy duty sealed connectors Series are rated IP67 and are dust and water-resistant when mated.
It is ideal for heavy equipment and vehicle power applications and is built to withstand the harshest and most challenging environments.
3. How to maintain?
Both sealed and unsealed connectors require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation and extend service life.
Appearance inspection: Periodically inspect the appearance to ensure that there is no damage. Sealed connectors need to check the condition of the plastic shell, plating, and seals, non-sealed connectors need to check the pins, jacks, and shells. If damage is found, it should be promptly repaired or replaced.
Cleaning: Clean the connector surface regularly to remove dust, dirt, grease, etc. Use a clean cloth or cotton swab, do not use cleaning agents containing solvents.
Testing: Sealed connectors require periodic testing of their sealing performance to ensure effective protection. Non-sealed connectors need to test the contact condition of the connection to ensure a good connection. Test tools such as pressure testers or multimeters can be used for these tests.
In addition, the following points need to be observed during use:
Correct installation: Follow the correct steps to install the connector to ensure proper operation.
Avoid overloading: Connectors should not be subjected to excessive current or voltage to avoid damage.
Regular inspection: Check the connector regularly to ensure proper operation.
In conclusion, sealed and unsealed connectors have different uses in automotive and industrial applications. Sealed connectors provide environmental protection, while unsealed connectors are used in less demanding conditions. The choice of connector depends on the specific application requirements.
Post time: Jan-19-2024