Electrical connectors are the unsung heroes of modern power and signal transmission systems, yet industry data reveals they’re responsible for 23% of unplanned equipment downtime. From manufacturing floors to automotive engines, these critical components face relentless stressors—vibration, humidity, temperature fluctuations—that lead to costly failures. This guide breaks down the five most prevalent failure modes, backed by 2025 technical standards and actionable prevention strategies to keep your systems running reliably.
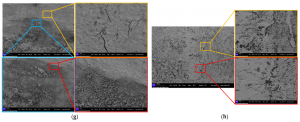
1. Contact Corrosion: The Silent Coastal Threat
Why It Happens: Metal contacts oxidize or sulfidize when exposed to moisture, salt, or industrial pollutants, increasing resistance and causing dangerous overheating. In coastal environments, uncoated copper contacts fail in 500 hours 58% of the time, according to salt spray tests.
How to Prevent It:
- Upgrade to Gold Plating: For high-reliability applications (like aerospace), specify a minimum 0.5μm gold plating to resist corrosion.
- Seal Out Moisture: Use dielectric grease in humid settings and opt for IP67+ rated connectors to block water ingress.
- Stick to Inspections: Follow IEC 60512-26-100 standards with 6-month inspection cycles to catch early corrosion.
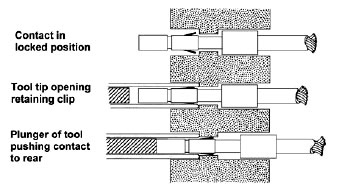
2. Pin Retraction & Deformation: The Automotive Industry’s Top Headache
In the automotive sector, no failure is more common than pin retraction or deformation. Misaligned mating during assembly and weak terminal retention force (less than 40N, per USCAR-2 standards) are the primary culprits.
Solutions That Work:
- Self-Aligning Designs: Choose connectors with ±0.5mm tolerance to accommodate assembly misalignment.
- Stronger Terminals: Upgrade to double-latch terminals, which boost retention force by 60%.
- Precision Assembly: Use vision-guided robots in production lines to eliminate human error during mating.
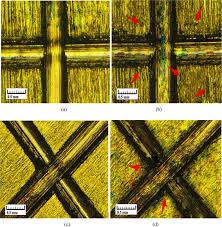
3. Insulation Degradation: When Plastics Break Down
Insulation materials like LCP and PPS can crack at temperatures above 150°C, while high-voltage connectors risk dangerous carbon tracking. Left unchecked, these issues compromise safety and performance.
A 3-Step Prevention Framework:
- Material Selection: Prioritize LCP over PA66 for better heat resistance.
- Thermal Testing: Ensure connectors pass 1000 thermal cycles with less than 10% resistance change (ΔR < 10%).
- In-Service Monitoring: Maintain insulation resistance (IR) above 100MΩ to prevent breakdowns.
4. Fretting Wear: The Hidden Cost of Vibration
In high-vibration environments—think industrial motors or aerospace systems—micro-movements as small as 3μm can generate 10Ω of contact resistance in just 200 cycles. This fretting wear gradually degrades connectivity.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Noble Metal Plating: Palladium-nickel (Pd-Ni) plating outperforms tin in resisting wear.
- Lock It Down: Use anti-vibration mechanisms like those in the MIL-DTL-38999 series for military-grade reliability.
- Monitor Trends: Track contact resistance over time to catch wear before failure.
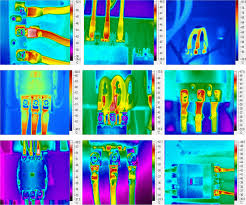
5. Overheating: The Leading Cause of Electrical Fires
Overheating occurs when resistance spikes, often due to loose connections. A temperature rise of 30K above ambient (ΔT > 30K) or a 15% resistance increase signals imminent danger.
Protection Protocol:
- Torque Verification: Ensure screw terminals are tightened to ±10% of specifications.
- Thermal Checks: Use infrared thermography during preventive maintenance to spot hotspots.
- Smart Connectors: Invest in 2025’s embedded sensor technology for real-time temperature monitoring.
2025 Industry Trends: The Future of Connector Reliability
The connector industry is evolving rapidly to tackle these challenges:
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT-enabled connectors are driving a 40% surge in predictive maintenance adoption, letting teams fix issues before they fail.
- Nanocoatings: New nanotech coatings reduce corrosion failures by 70% in harsh environments.
- High-Speed Demand: The automotive sector now requires 10Gbps connectors to support advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
By addressing these five failure modes with the latest standards and technologies, you can drastically reduce downtime and improve system safety. Whether you’re designing for coastal humidity or automotive vibration, the right prevention strategy starts with understanding the risks—and staying ahead of 2025’s innovations.
Post time: Jun-27-2025