An interesting phenomenon found that in many of the original orange high-voltage connectors, used in vehicles for some time, the plastic shell appeared white phenomenon, and this phenomenon is not an exception, not family of the phenomenon, the commercial vehicle particularly.
Some customers asked me whether this affects their use. Is there any risk? Does it affect the service life?
Before answering this question, list a few questions to find the answer:
1. Why is it necessary to use orange color for high voltage connectors? Is it possible not to use it?
2. What kind of material is the connector usually a plastic shell? Where does the orange color come from?
3. Because of the use of special scenarios,? Is there any problem with long-term application?
4. What does this cause us to think about and what do we need to pay attention to?
Why do high voltage connectors need to use orange color? Can we not use it?
The use of orange as a warning color for high voltage is considered an “international practice”, for example, the U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) has adopted orange as the required color for high voltage cables; since the late 90′s when HEVs were gradually popularized to EVs, orange has been used as a high voltage warning color code for xEVs, which is used to denote high voltage wires and connectors. high-voltage cables and connectors; this eye-catching color-coding system identifies which high-voltage unit components should not be touched without proper safety training and personal protective equipment.
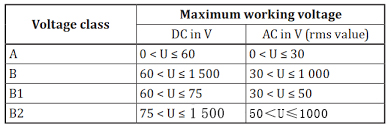
What is automotive-grade high voltage? The “automotive grade” “high voltage concept” is usually “voltage class “B” according to the definition of ISO 6469-3, generally with an operating voltage of >60 V and ≤ 1500 V DC or 30 V and ≤ 1000 V AC. > 30 V and ≤ 1000 V AC, according to the standard “High-voltage bus cables which are not located in the housing shall be identified by a cover with the color “orange” The bus, in this case, refers to the assembly, which also contains the connectors;
In terms of connector standards, whether it is the major OEM’s standards, or Europe has been dissolved “LV series standards” or similar USCAR standards, (LV215 216 USCAR20 SAE1742, etc.) have stipulated that the high-voltage connector color coding orange and the color card number stipulates the requirements of RAL 2003, 2008 and 2011; of which RAL 2003 is the brightest, RAL 2011 is more reddish and darker, and RAL 2008 is in between. Requirements are generally defined as RAL 2003, 2008, and 2011; of which RAL 2003 is the brightest, RAL 2011 is more red and darker, and RAL 2008 between the two, while orange needs to meet the color of more than 10 years without metamorphosis.
So the color of orange is the basic law of the road, if it is made of metal, usually also needs to be marked in the obvious area of the high-voltage warning label, so can not be orange? Normally not, because the relevant safety regulations may be rejected.
What kind of materials are used for connectors with plastic shells? Where does the orange color come from?
Connector shells are usually made of polyurethane materials, commonly used PA66 PBT, etc., the general plastic shells need to meet the requirements of the system insulation, and at the same time need to have certain physical characteristics, such as sufficient strength, tear resistance, toughness, etc., but also need to have the characteristics of flame retardant, so the general CTI value has special requirements, usually, manufacturers will use nylon materials to increase the appropriate Usually, manufacturers will use nylon material with appropriate glass fiber as its material, such as PA66+30%GF_V0 or PBT.
The orange color is generally formed in 2 ways, one is white plastic particles plus a certain percentage of color powder blending, generally is custom color, the latter color is more stable, and the corresponding cost is also higher, the general material manufacturers have to meet the corresponding standard requirements of the custom color, such as BASF, Celanese and so on.
Because of the use of special scenarios,? Are there any problems with long-term applications?
The problem at the beginning of the article is located in the battery box outside, exposed, location is exposed to sunlight all year round, and closer to the wheel, the wheel inertia of corrosive pollutants thrown up a certain percentage attached to the material, based on this, first of all, the probability of whitening is greater because of its prolonged exposure to high temperatures and sunshine, accelerating the speed of its aging, which leads to whitening, and at the same time, UV and other rays will be caused by chemical reactions and material surface, resulting in accelerated material whitening. At the same time, ultraviolet rays and other rays will also cause a chemical reaction with the material surface, thus leading to accelerated material embrittlement and whitening, in addition to exposed and close to the vehicle will make it more likely to be corroded by the acid-containing pollutants, which will lead to the accelerated decomposition of material molecules in the acid under the support of the chemical reaction whitening.
Overall, the whitening of the material means that there is a potential risk of “embrittlement” and “degradation of electrical properties”, which will affect its service life and increase the chance of product failure compared to normal connectors, such as cracking after impact with foreign objects, such as stones. Compared with normal connectors, there are more chances of product failure, such as being more susceptible to cracking after the impact of stones and other foreign objects, having poorer impedance when wet, and being more susceptible to breakdown.
To trigger us to think about what needs to be paid attention to?
From the perspective of the development of high-voltage connectors, connectors toward more miniaturization, integration (materials easier to include more electrical contacts) more lightweight (more compact structure, smaller size, thinner thickness, etc.) trend, this for the product underlying technology research and breakthroughs put forward higher requirements; for example, more abrasion-resistant contact terminals (plating materials, substrate selection, and other research) and so on.
At the same time, plastic materials also put forward higher requirements, a broader working environment throughout the life cycle requirements, higher CTI requirements, and 0.4mmV0 under the requirements of the electrical properties, the entire life cycle of the stability of the color, materials, high heat resistance, high thermal conductivity of the material, the need to focus on the material additives on the electrical corrosion of the contacts, the physical stability of the material at the long-term use of the force structure Stability of material application in harsh environments, etc…
Post time: Feb-28-2024