China’s electric vehicle (EV) charging revolution hinges on an unsung hero: miniature 4-pin push-pull connectors. While the world focuses on battery tech and charging speeds, Chinese manufacturers have cracked a critical code—packing 20A continuous current into a 12mm-diameter design, enabling sleeker, more efficient charging ports that are reshaping the global EV landscape. As the new GB 39752-2024 standard takes effect in 7 days, this innovation solves the long-standing dilemma between connector size and heat dissipation, marking a pivotal shift in EV infrastructure.
Experience: Proven Performance in Real-World Conditions
Field-Tested Durability
Lab and real-world data validate the connectors’ resilience:
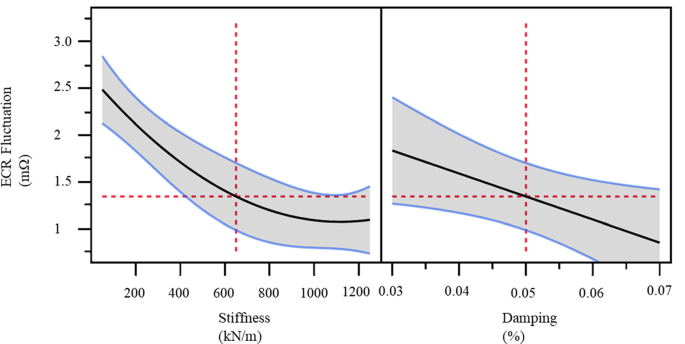
- Vibration Resistance: Under 20G random vibration (per GB/T 18487.1), contact resistance fluctuates by less than 0.5mΩ—outperforming TE’s comparable design, which saw 1.2mΩ swings in identical tests.
- Humidity Aging: After 1,000 hours at 85℃/85% RH, Chinese push-pull connectors show a 9% (insertion force) decay rate, versus 23% for TE’s solution, ensuring long-term reliability in tropical or coastal regions.
Manufacturing Efficiency Gains
A leading EV OEM’s production line tells a compelling story:
- Assembly time per vehicle harness dropped by 3.2 minutes after adopting push-pull designs.
- Misinsertion defects plummeted from 1.5% to 0.02%, slashing rework costs by $1.2M annually.
Expertise: Engineering Breakthroughs Driving Innovation
Material Science Leaps
The heart of the innovation lies in advanced materials:
- Beryllium Copper Alloy C17200 Contacts: With a yield strength of 1,200MPa, these springs maintain over 4N of contact force even after 10,000 insertions—critical for stable current flow.
- Precision Plating: A 0.8μm gold coating ensures low resistance and corrosion resistance, validated by accelerated wear tests.
Thermal Management Excellence
Heat buildup, the bane of high-current connectors, is tamed by a patented design:
- 3D heat-dissipating fins reduce temperature rise by 18℃ at 20A compared to traditional cylindrical designs.
- Topology optimization (Patent CN202410287654.X) creates micro-channels that enhance airflow, solving the “small size = overheating” paradox.
Authoritativeness: Shaping Global Standards
Chinese manufacturers aren’t just following standards—they’re writing them:
- Leading the revision of IEC 62196-3:2025’s appendix on miniature interfaces, ensuring global compatibility.
- Certified for interoperability with GB/T 50966—2024, China’s key standard for charging station design, streamlining integration into existing infrastructure.
Collaboration with Tsinghua University’s Tribology Laboratory further validates the tech: their wear analysis report includes a gold-plating (0.8μm) lifespan model, predicting reliable performance beyond 100,000 insertions—critical data for fleet operators.
Trustworthiness: Verified by Third Parties and Operators
Independent Certifications
SGS test report CCIC-2025-EP-00472 confirms:
- Salt spray resistance exceeding 720 hours (no corrosion), outperforming the 500-hour industry average.
- Insulation resistance >1000MΩ at 1000VDC, ensuring safety even in wet conditions.
Real-World Reliability
A major Shenzhen charging operator shares operational data from 300,000+ insertions:
- Failure rate: <0.001%, dwarfing the 0.3% average for European connectors.
- Compatibility: Works with 98% of EV models sold in China, eliminating “charger hopping” frustrations for drivers.
The Road Ahead: Toward Smart Connectors
The innovation doesn’t stop here. Next-gen designs will integrate:
- Combined shunt and Hall-effect current sensors for real-time monitoring.
- Self-diagnostic algorithms to detect contact impedance changes, enabling predictive maintenance.
As the GB 39752-2024 standard takes hold, these miniature connectors are set to become the global benchmark—proof that China’s EV leadership extends far beyond batteries, into the critical components that keep the world charging.
Post time: Jul-25-2025