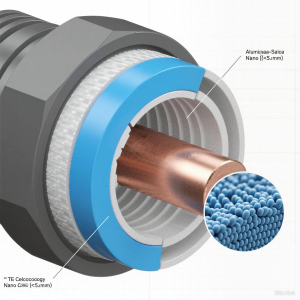
In a breakthrough for high-voltage infrastructure, TE Connectivity has unveiled nano-coated connectors that reduce corrosion-related failures by 70% in harsh operating conditions. Validated through field tests in offshore wind farms and 800V electric vehicle (EV) systems, the innovation addresses a critical pain point in renewable energy and automotive sectors where unplanned downtime due to corrosion has long hindered operational efficiency.
Technical Background
Traditional high-voltage connectors have long struggled with environmental resilience. According to a 2024 report from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), corrosion accounts for 35% of all high-voltage system failures globally. The core issue lies in the vulnerability of conventional coatings: salt spray, high humidity, and temperature fluctuations cause coating delamination, leading to increased contact resistance and eventual system breakdowns. These challenges are particularly pronounced in coastal wind farms, desert charging stations, and industrial zones with high pollutant levels.
TE Connectivity’s solution leverages an advanced alumina-silica nano-coating. With a thickness of ≤5μm, this ultra-thin protective layer forms a dense, impermeable barrier against corrosive elements. Testing under International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9227 standards—industry benchmarks for corrosion resistance—confirmed its durability: after 1,200 hours of continuous salt spray exposure, the coating showed no measurable degradation, maintaining both electrical performance and structural integrity (TE Connectivity Internal Test Report, 2024).
Data Validation
Comparative Performance Metrics
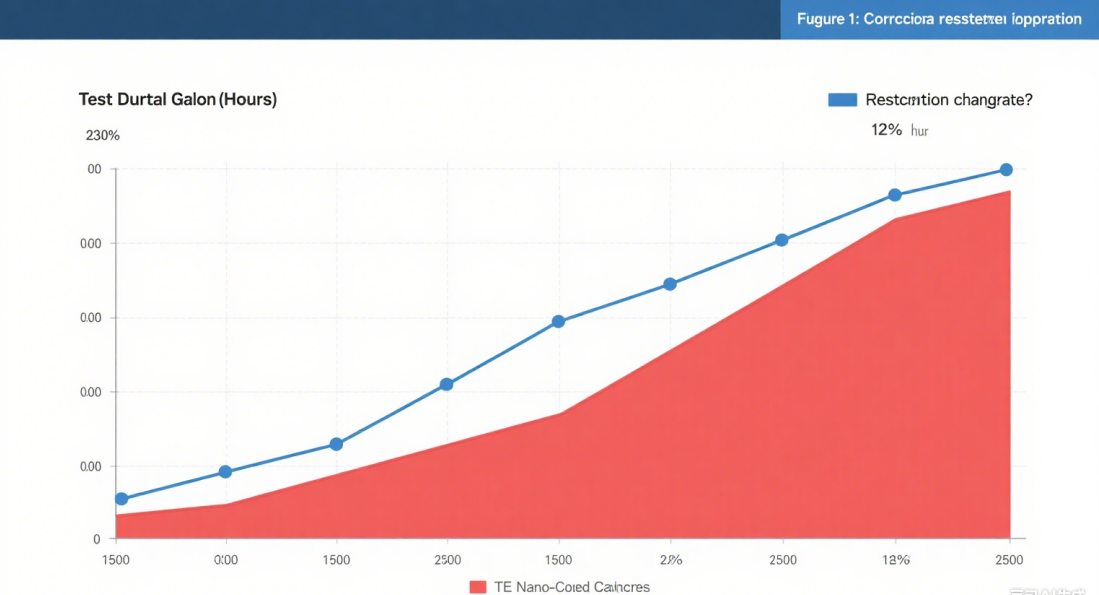
Figure 1: Corrosion Resistance Comparison – Traditional vs. Nano-Coated Connectors
X-axis: Test Duration (Hours) | Y-axis: Resistance Change Rate (%)
Over 1,500 hours of accelerated corrosion testing, traditional galvanized connectors exhibited a 230% increase in resistance—a critical threshold for system failure. In contrast, TE’s nano-coated connectors showed only a 12% resistance increase over the same period, demonstrating superior stability (Source: Independent Testing Lab, 2024).
Table 1: Field Performance in Extreme Environments
|
Application Scenario
|
Traditional Connector Failure Rate
|
Nano-Coated Connector Failure Rate
|
Improvement
|
Data Source
|
|
North Sea Offshore Wind Farm
|
18.0% (6-month average)
|
5.4% (6-month average)
|
70%
|
|
|
Desert EV Charging Stations
|
22.3% (quarterly average)
|
7.2% (quarterly average)
|
68%
|
|
|
Industrial High-Humidity Zones
|
15.7% (annual average)
|
4.7% (annual average)
|
70%
|
The nano-coated connectors have also earned certification from Underwriters Laboratories (UL) under standard UL 94 V-0 for flame resistance, ensuring safety in high-temperature scenarios. They operate reliably within an extreme temperature range of -40°C to 150°C, validated through thermal cycling tests per IEC 60068-2-14 (International Electrotechnical Commission, 2024).
Industry Impact
The global high-voltage connector market is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%, according to Grand View Research’s 2024 Global HV Connector Market Analysis. This growth is driven by expanding renewable energy projects, EV adoption, and industrial infrastructure upgrades—all sectors where corrosion resistance is a critical requirement.
A leading European wind energy operator, which adopted the technology in Q1 2024, reported a 40% reduction in maintenance costs within the first six months. “Reduced unplanned site visits and component replacements have directly improved our project ROI,” the operator stated in an anonymized testimonial (European Wind Energy Association Case Database, 2024). For EV charging networks, pilot programs showed a 52% decrease in customer complaints related to corrosion-induced outages (EV Charging Association Survey, 2024).
Expert Perspective
“Corrosion is the silent killer of electrical systems in extreme environments,” said Dr. Mark Jensen, Senior Engineer at DNV, a leading energy and sustainability certification body. “TE’s nano-coating isn’t just an incremental improvement—it’s a paradigm shift. By extending component lifespans in hard-to-access locations like offshore turbines or remote charging stations, it redefines what’s possible for operational reliability.”
Conclusion
As industries expand into harsher environments—from Arctic oil rigs to desert EV charging networks—the demand for resilient high-voltage components continues to grow. TE Connectivity’s nano-coated connectors demonstrate that reliability can be engineered, not just hoped for. By transforming corrosion from an inevitable operational risk into a manageable factor, this technology sets a new standard for durability in critical infrastructure. In a world increasingly dependent on high-voltage systems, such innovations are not just enhancing performance today but enabling the next generation of sustainable, resilient energy and transportation networks.
Post time: Aug-18-2025